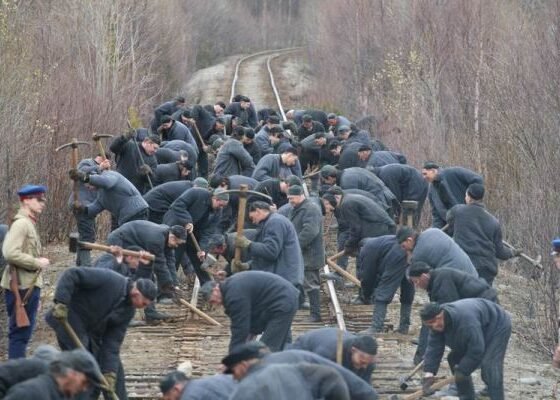
(GW Today) “Dr. Orttung is the principal investigator for a five-year $561,377 project funded by the NSF.” With support from the National Science Foundation, George Washington University researchers are working to better understand the changing nature of the Arctic, a region that is being reshaped by climate change and natural resource development.
GW faculty and students have received three separate grants worth a total of nearly $2.4 million from the NSF in order to conduct interdisciplinary research on Arctic issues including climate change, oil and natural gas development and physical changes to Arctic permafrost, soil that has remained below freezing for two or more years.
The Arctic is expected to be a major new source of oil and natural gas as more fields, both onshore and offshore, become accessible to drilling.
“There’s a huge amount of resource development planned for the Arctic,” said Robert Orttung, an associate research professor in the Elliott School of International Affairs and the assistant director of the Institute for European, Russian, and Eurasian Studies. “As it warms, obviously there’s more access to oil and natural gas and other minerals there.”
Dr. Orttung is the principal investigator for a five-year $561,377 project funded by the NSF to build a Research Coordination Network of scientists and policymakers studying Arctic urban centers. The project, which will focus on Russia, is a multidisciplinary, international effort to examine the interconnections among resource development, climate change and evolving demographic patterns. The goal is to provide advice to policymakers on how to develop Arctic oil and natural gas deposits and their related infrastructure in a way that produces minimal impact on the environment. The project will run for the next five academic years.
“We’re looking at the connections between resource development, climate change and human movement into this area,” Dr. Orttung said. “All these things are happening in the cities in the Russian Arctic.” […]
See the article | © GW Today